The technology industry thrives on buzzwords and acronyms. As a result, something new will shroud the domain every few years, causing a paradigm shift that will change the tech world. One such term doing rounds in the industry is “Edge Computing.” While edge computing isn’t entirely a new concept, and people have been hearing about the edge computing trend for almost a decade now, the overall picture is undergoing an evolution.
For many years, cloud computing denominated the market and has been the primary data storage solution for several reasons, including accessibility and scalability. With cloud computing, it’s possible to access servers anywhere in the world.
However, the drawback of cloud servers is, it can be challe犀利士
nging to customize them depending on the company’s specific needs. Moreover, as more and more data are arising, the storage and processing of such vast data can overwhelm the systems. This is where edge computing is bridging the gap.
For this reason, edge computing trends in 2023 will create a much more significant influence.
Understanding Edge Computing
Edge computing is data processing at the edge of a network, close to where data gets generated and the user is, instead of in any random centralized location. This type of approach enables more responsive and speedier decision-making. With edge computing, the data can get processed directly and swiftly instead of leaning on the cloud servers to process information and wait for it to return.
In a nutshell, the idea is to position computing instruments closer to the user or the device, literally at the “edge” of the network, in comparison to placing it in a hyper-scale cloud data center many miles away from the “core” of the network. As a result, the edge approach helps reduce latency and facilitates data processing close to the source.
According to the Red Hat technology evangelist Gordon Haff, “Edge computing can apply to anything that involves placing service provisioning, data, and intelligence closer to users and devices.”
As a result, edge computing is emerging as a big market and continues to grow. The size of the global edge computing market will explode to this level by 2027, reaching $43.4 billion at a compound annual growth rate of 37.4 percent, according to Grand View Research.
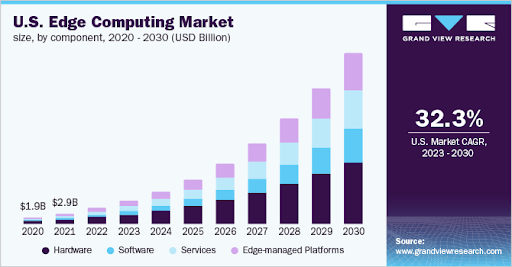
But what does this growth entail for enterprises and organizations? For one, they should prepare for an edge computing environment. Companies looking for opportunities to process data locally to reduce latency must adapt to edge computing trends in 2023 to beat the competition and stay relevant.
Edge Computing Trends In 2023 Shaping The Future Technological World
Edge computing helps businesses rely less on transmitting data back to a central location, processing it, and getting a response. Due to this, the processing can alternatively occur in nearby edge data centers.
As a result, organizations across niches should keep an eye on disruptive technologies that support and surround edge computing and how they’re using edge computing technologies.
To help keep up with edge computing trends in 2023, here are some noteworthy developments in this space to pay attention to for business growth.
5G is pacing up
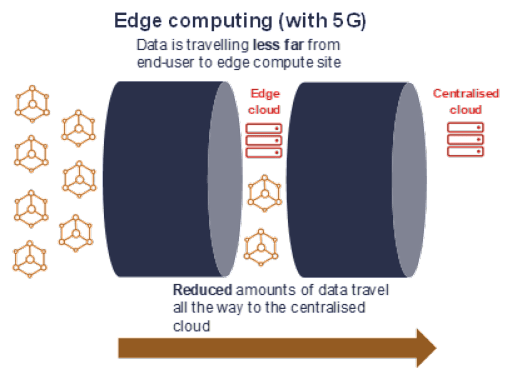
Excluding the people who consider 5G as a peril that causes Covid or impacts brain health, everyone else understands that 5G translates to faster data processing.
As a result, many countries like US and China are embracing the expansion of 5G networks. And the numbers indicate an upward curve, too. According to Ericsson’s report, the US witnessed a half-billion connections at the end of 2021 and predicted that the numbers would reach 3.5 billion by 2026. In another research by Omdia, 5G connections are expected to nearly double in 2023, reaching 2 billion connections by the end of the year. They further estimated that connections will reach 4.8 billion by the end of 2026.
As 5G processes data faster and creates a broader pipe to carry data, it can deliver the ultra-low latency required for many use cases. These applications include the extensive deployment of self-driving automobiles, virtual reality, and the metaverse.
Although edge computing is potent enough to reduce latency by keeping compute resources near the endpoints producing data, 5G used with edge computing further reduces latency to support use cases where close to real-time processing is indispensable. Delivering more edge computing at speed can be a key to advanced business functionality. Many businesses could benefit from edge computing and 5G to get an edge over competitors.
The edge: An extension of the cloud
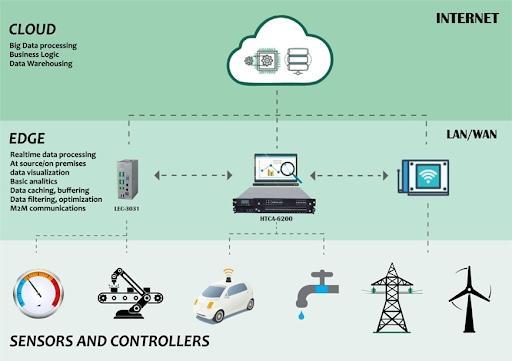
Edge computing is practically the next stage of distributed computing evolution. It tackles the problem of taking the computing experiences currently running in big data centers or a cloud and putting them in several small data centers in close range to the end user.
It’s where edge computing shines and helps to push the limits, bringing the apps closer to where the users are.
But it doesn’t imply that the edge will eliminate the need for cloud computing. Instead, edge computing will be an extension of cloud computing. Edge computing is more spread out and lightweight.
While some data processing will take place on edge devices, for example, smartphones and tablets, or via several AI chips that Tesla is integrating into their cars, big processing will still rely on more potent and vast data centers like the cloud.
State of the Edge emphasizes that “as the demand for edge applications grows, the cloud will drift closer to the edge.” As a result, the edge will help improve user experience and act as an extension of the cloud.
Combining IoT technology and the edge computing
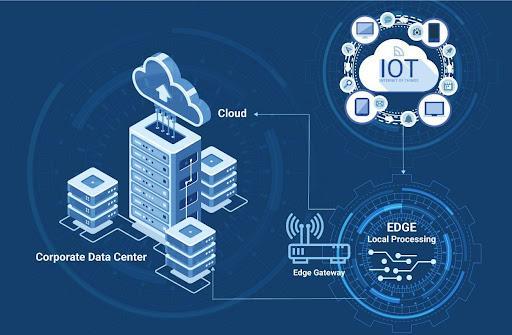
Edge computing is considered a game changer for the IoT as it facilitates IoT devices to get utilized independently, store, process, and analyze data in IoT locally rather than leaning on a centralized server. Such provision improves the efficacy of IoT devices and makes the deployment of topologies and new devices possible.
The Internet of Things (IoT) can be described as linking physical things to the Internet. It consists of devices or systems automatically exchanging data over an internet network. Some examples of IoT include sensors, smart homes, autonomous vehicles, smart watches, etc.
Edge computing with IoT allows organizations to deploy workloads on IoT hardware by enhancing flexibility, enabling new use cases, and improving performance. This also includes low latency and high throughput data, which was impossible with the traditional IoT. As a result, it’s among the top edge computing trends in 2023 that organizations are willing to adopt.
According to the 2021 IoT and Edge Commercial Adoption Survey report, the following shows the acceleration in utilizing IoT and edge computing solutions.
- Businesses are open to adopting IoT technologies at an augmented rate, and edge computing adoption is also accelerating. The report indicates that 53% of respondents are deploying IoT solutions. Currently, 24% plan to deploy and 18% consider deployments.
- The interest in adopting edge computing is also rising. 53% of companies are planning or already adopting edge computing, and another 20% are considering using edge computing.
- Further, there is a shift to increased investment in IoT & Edge. 33% of respondents project spending between $100K - $1M in 2023. 12% anticipates spending over $10M in 2023.
Improved agri-tech with edge
Agri-tech has been growing in importance for years. The global agri-tech market stood at US$ 19,542.7 million in the year 2021, and reports indicate it can grow up to US$ 46,372.5 million by 2030, at a CAGR of 17.3%.
The year 2023 is likely to give a whole new meaning to farming. Better edge computing can boost the efficiency of agri-tech, enabling data processing at a distance and bearing better, more cost-effective farming results. Here are the use cases of edge computing in agri-tech.
- The Agribots acting as autonomous tractors and robotic machinery can work on autopilot mode, communicating with locally placed sensors to access necessary data and insights about the nearby environment.
- The intelligent tools can execute multiple tasks, like watering and weeding specific field areas or even autonomously harvesting crops as required.
- A greenhouse or entire farms can run on autopilot using IoT edge computing.
- Further, remote sensors using edge networks can gather and analyze data regarding weather conditions and the environment to predict potential natural disasters. If there are surefire signs of trouble, it can immediately alert the control center, allowing farmers to take timely measures to protect their crops from harsh outcomes.
Faster on-site machine learning
Edge computing makes machine learning at remote sites more feasible. With edge computing, it’s possible to position machine learning-powered applications physically closer to data sources. The data centers positioned at the network edge ingest and analyze data streams from numerous sources providing helpful context for critical decisions.
It helps determine the possibilities of processing data locally or at a more robust cloud data center. It’s important to note that edge devices send data to the cloud data center, but closer edge computing allows you to scan the data first and send it only when necessary.
Further, this amalgamation of edge and machine learning ramps up data processing and allows you to respond to swiftly changing conditions in real-time, ensuring to add value in real-world use cases and scenarios that work on fast data processing.
If edge computing becomes relatively ubiquitous in 2023, it will normalize machine learning at speed and distance.
Furthermore, it will develop the trust of customers and business employees in the uses and results of machine learning and AI by decreasing the latency in the process to reasonable and feasible levels.
Cybersecurity at the edge
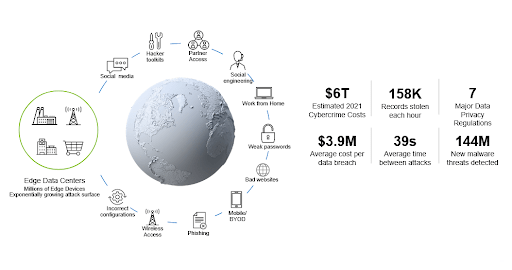
Cyber attacks are a concrete reality. The technological world witnessed a 50% rise in Cyber attacks in 2021, and the problems continue to increase. On the other hand, edge computing integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) carries data decentralization and computing to new heights.
In addition, it also raises prospects and challenges linked to privacy and security. For many organizations, it can enhance cybersecurity threats by growing a broader attack surface to potential security risks beyond traditional data centers and their firewalls.
With billions of edge devices and sensors spread worldwide that will all be connected to the Internet, these organizations should consider protecting edge devices from attack and assess their cloud and network security.
So, it’s apparent to expect AI will get applied more to cybersecurity in 2023. With the help of AI, it’s possible to pass the log data produced from IoT networks through intelligent security models for alerting against suspicious behavior and for information security teams to take quick action.
Edge-powered future - Summing up
Edge computing has the potential to help individuals and organizations handle information and use their devices more effectively. Whether your company heavily focuses on gathering consumer data or reducing latency through 5G-edge computing, 2023 can bring significant business benefits.
Edge computing supports the evolution of emerging technologies like autonomous driving, agri-tech, healthcare, and even today’s booming technologies like IoT. Further, 5G is helping to improve the ultra-low latency required for many edge computing use cases, taking the edge to new heights.
As edge computing allows things to get processed and analyzed faster than ever, knowing its use cases and how businesses can use it to their advantage can be a game-changer. In several sensitive industrial environments, it could predict disasters and save lives.
Undoubtedly, edge computing is on the path to revolutionizing the future of technology. Now, it depends on the businesses whether they are wise and proactive enough to get the best out of it.














Leave a Reply