Surgeons, dentists, and students are you aware that 3D printing is becoming one of the medical industry's primary tools? Now you might say, "Duh! Vivek…This is a very dumb question.
However, I would like to say that in today's context, it is imperative.
Specifically, when we talk about 3D printing in medicine, many new medical projects are developed employing resin, metal 3D printing, or plastic.
3D printing in medicine improves the daily lives of medical professionals, enabling them to save more and more lives daily.
In the forthcoming sections of this write-up, we will look at a step-by-step guide on the impact created by 3D printing in the healthcare domain.
So, without further ado, let's get started with the definition of 3D printing.
Table of Contents
1. What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing, popularly known as additive manufacturing, is the process of developing physical objects from a digital file by integrating multiple layers of material. Alternatively, even various materials can be used to create a single structure.
This structure is based on a computer-aided design file's input in a format compatible with the 3D printing hardware.
3D printing was first invented by Chuck Hull, co-founder of 3D Systems. Since then, this concept has grown by leaps and bounds to integrate 15 methods or technologies that combine all these layers. All of them are commonly known as 3D printing. I hope you have now understood what 3D printing is.
Now let’s move forward to the next section.
2. What Is 3D Printing In The Context Of The Healthcare Domain?
3D printing is primarily an apt choice for the medical industry since it is research-based, out-of-the-box, and fast-moving.
With the advancement of technology, we are seeing significant growth in precision and personalized medicine. This makes a case for strong demand for customized and patient-specific medical applications explicitly tailored to an individual or their anatomy, like 3D printed organs.
3D printing drives the production of these custom-made products and devices wholly or partially.
Some of examples of the actual and potential use of medical 3D printing include:
- Customized prosthetics and implants
- Pharmaceutical research like drug dosage forms and discovery
- Tissue and organ fabrication
- Personalized medical products and types of equipment
Now that we have looked at what 3D printing is, in the next section, we will divert our attention to the best ways to utilize medical 3D printing.
3. How Can 3D Printing Be Used In Medicine?
Utilizing medical imaging with the aid of 2D or 3D onscreen technology limits radiologists and surgeons from visualizing complicated pathologies and abnormalities.
Thus, we are seeing an increasing number of radiology teams and surgeons employing medical 3D printing to develop 3D 1:1 models of anatomical areas, replicated precisely from patients' scans, in the form of 3D-printed organs. This can be held in hand and utilized for preoperative cutting, collaborative team working, and planning.
These anatomical models come in handy for performing patient communication and consultation to showcase and explain to patients their medical conditions and the medical-surgical procedures it will involve.
3D printing in medicine is even employed in surgical education by providing medical students and junior doctors the opportunity to check tumors precisely, lesions, fractures, and other abnormalities.
Now that we have looked at the best ways to utilize medical 3D printing in healthcare let's divert our attention to medical 3D printing benefits.
4. 3D Printing Benefits In Medicine
1. Helps in performing complex operations
3D printing in medicine plays a vital role in training prospective doctors and preparing them for actual operations. 2D images are useful. However, they provide little visualization and do not represent an actual human part. Whereas 3D printing in medicine provides models that look realistic and mimic human parts, for example, 3D printed organs. This aids in making the operational process more precise and useful.
2. Utilizes advanced technology
Prospective doctors can practice on 3D printed organs, which is much more precise than an example training on animal organs. By training on human-like, 3D-printed parts enhances the quality of skills doctors get during practice.
3. Provides intricate care
3D printers create low-cost prosthetics wherever people require them. A prime example of that is war-torn countries. They are the cost-effective solution for people who can ill afford to purchase a prosthetic. Low-cost medical equipment is also critical for poverty-stricken countries. There are certain areas where road infrastructure is too bad to deliver medical equipment. This is where 3D printing makes it seamless to print the desired equipment in those villages without regularly transporting them.
4. Reduces costs and time spent waiting to receive a new medical device from external suppliers
With the help of 3D printing, you can 3D print medical & lab equipment. It even enables you to 3D print plastic parts of the equipment. This drastically reduces costs and time spent on receiving a new medical device from external suppliers. On top of that, the manufacturing process and further applications are also effortless. In turn, making the equipment more readily available becomes easier and even allows low-income or hard-to-access areas to procure 3D-printed medical equipment more efficiently.
5. Aids you in customizing the 3D-printed organs
Everyone knows today that making prosthetics the traditional way is expensive as they need to be personalized to the individual. With the help of 3D printers, you get the freedom to select different types of designs, forms, sizes, and colors of their prostheses. This ensures every 3D printed piece is personalized precisely. Also, 3D printing in medicine enables prosthetics to be more extensively available at a fair price works in its favor.
Let's now divert our attention to some practical examples of 3D printing in medicine.
5. Use Cases Of 3D Printing In Medicine
Some of the use cases of 3D printing in healthcare have breached a new benchmark, and what makes medical professionals so excited about this breakthrough technology in medicine.
Cost-effective prostheses
Every year, hundreds of people lose a limb; however, only a small section gets access to the prosthesis to recover its function. Now, simple prostheses are only accessible in a few sizes, so patients have to try to make the most of them. While custom-fit bionic devices designed to replicate the motions and grips of real limbs that depend on muscles in a person's residual limb to control are very expensive. This makes them only accessible to patients with the best healthcare insurance in developed countries. This mainly has an adverse effect on prostheses in children. With time as they grow, children inevitably outgrow their prostheses and need expensive repairs.
There is a lack of manufacturing processes that can cost-effectively produce custom parts. However, with advancements in technology today, prosthetists are taking advantage of 3D printing's much-noted design freedom to undermine these financial barriers to treatment.
One of the prime examples of that is Handsmith, a company that helps people who need a bionic prosthetic; however, they are not eligible for insurance claims or cannot afford one on their own. Here's a video that showcases how Handsmith is changing an industry and lives using 3D-printed prosthetics.
Corrective insoles & orthoses
Some of the financial difficulties we saw in the above point also apply to insoles and orthoses. Like many other patient-specific medical devices, custom orthoses are often inaccessible due to their high price, and it takes weeks or even months to get manufactured. However, when you utilize 3D printing, these limitations are no longer applicable.
Let's now look at a practical live example of Matej and his son Nick.
Nik was born prematurely in 2011, resulting in cerebral palsy, affecting approximately twenty million people globally. Matej was surprised to see his son's unwavering will, which inspired him to transcend his medical condition's limitations. However, he had to choose between two things.
Either he has a standard, pre-made orthosis that could be inadequate and uncomfortable for his son or an expensive custom solution that could take perhaps weeks or even months to be delivered, only to be made obsolete by a growing child.
He decided to take matters into his own hands and look for out-of-the-box solutions. With the freedom provided by digital technologies like 3D scanning and 3D printing, Matej and his son Nik's physical therapists could experiment liberally and develop an innovative workflow for ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs).
Thanks to the custom-made 3D printing orthosis, Nik got the support, comfort, and correction precisely where it was needed. It aided Nik to at last take his first independent steps. This custom orthotic device consists of a highly adjusted finish of high-end orthotics at a price that did not hurt the pockets of Matej and with absolutely zero further adjustments needed.
Here's a YouTube video that enumerates the tail of Matej and his son Nik's story.
Now that we have looked at a couple of medical 3D printing cases in the healthcare domain let's focus on the last section of this write-up: companies that have made their names in the 3D printing medicine field.
6. 3D Printing Companies In Medicine
Here are some of the best 3D printing companies in medicine.
1. Isinnova
Isinnova, a Brescia-based engineering company, has become the town's talk, and Cristian Fracassi, the CEO of the company, quickly responded to the shortage of respiratory valves required. To connect the COVID-19 patients to the machines, the company employed 3D printing, which saved patients' lives.
The exciting part is Isinnova couldn't have done it all alone. The company initially collaborated with physicist Massimo Temporelli, founder of FabLab. They started manufacturing valves within the space of 6 hours. Next, the company collaborated with the local manufacturer, Lonati, to mass-produce the valves.
2. Prusa
Prusa, the maker of the Original Prusa i3 MK3S 3D printer, is researching solutions at excellent speed to make a difference in this COVID-19 crisis. Within three days, it developed dozens of face shield prototypes. Two of which got verified by the Czech Ministry of Health.
The company has also integrated Prusament PETG Orange for PPE into their e-shop. It is made up of high-quality PETG material ideal for producing the shields like the headband and chin parts. Prusa kept pushing hard, and now it has joined hands with 3M and GE Healthcare and commenced printing Prusa's protective shield design.
3. Voodoo Manufacturing

Voodoo Manufacturing is a Brooklyn-based firm that runs two 3D printing factories with more than 200 machines. The company is putting in efforts to develop personal protective equipment, nasal swabs, replacement parts for ventilators, and other needed devices. It plans to print a minimum of 2,500 face shields every week.
4. Winsun
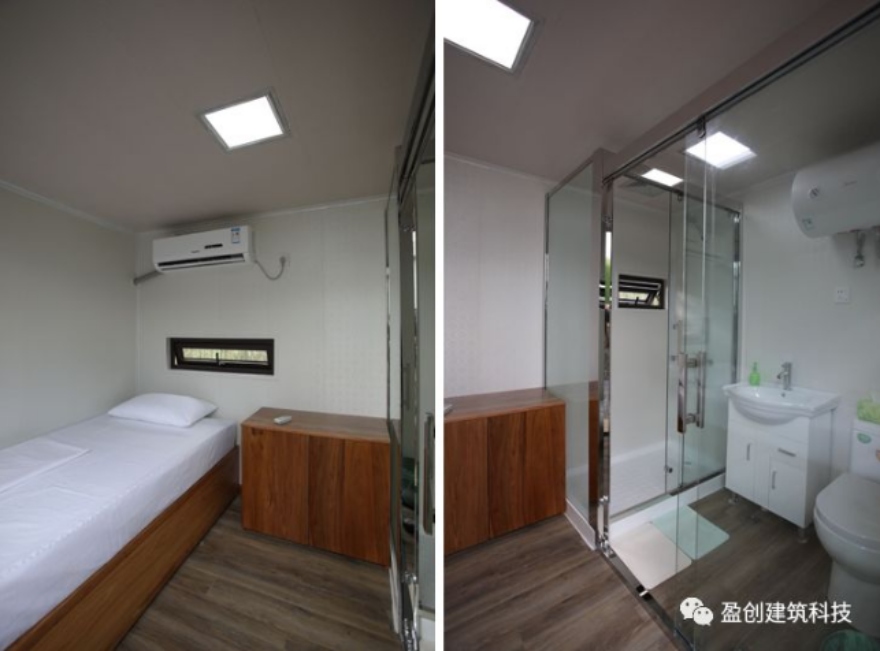

Winsun is an architectural 3D printing company giving a new direction to 3D printing in medicine during the pandemic. Based in China, the company has already dispatched 15 3D printed quarantine rooms to Xianning Central Hospital in the Hubei Province.
5. Formlabs

Formlabs is a 3D printer maker. The company has worked with medical experts at USF Health in Tempa and Northwell Health to swiftly develop and test nasal swabs. The company was able to create the swabs at the Ohio facility swiftly. The reason is that it was already registered with the FDA to manufacture certain medical products.
On top of printing test swabs, Formlabs is also validating designs for other test kit components, respiratory masks, and face shields.
7. Future Of 3D Printing In Medicine (Final Words)
Over time, we are now seeing highly accurate, cost-effective 3D printing processes in medicine, like desktop stereolithography decentralizing access to advanced technology.
This, in turn, is empowering healthcare professionals to develop cutting-edge clinical solutions. It also helps them to create custom devices swiftly and enables physicians to deliver brand-new treatments globally.
As 3D printing in healthcare continues to evolve, it will pave the way for personalized care and the creation of high-impact medical applications.
If you are curious about the future of 3D printing, here's an article about the weirdest 3d printed things!













Leave a Reply