Load balancing can assist with optimizing your cyber security and monitoring tools in numerous ways. It can help individuals and companies:
- Counter DDoS attacks
- Utilize SSL offloading
- Leverage WAF
- Streamline user authentication
- Prevent performance degradation
- Implement advanced redundancy schemes
- Facilitate network infrastructure expansion
We all know change is the only constant in the world of technology. For networks, that means dealing with ever-increasing speeds and traffic volumes while minimizing network downtime.
Load balancing is an irreplaceable component for enterprises that are looking to bolster their security from all sorts of external threats.
Undoubtedly, analyzing and scaling enormous data traffic by monitoring appliances is essential. High monitoring capabilities are required when there is a lot of incoming traffic since it increases computational constraints exponentially and overwhelms the monitoring instruments.
A website or commercial application ultimately reaches the point when a single server cannot handle the whole workload. Organizations distribute the burden among several servers to handle the demand. This procedure, known as load balancing, stops a single server from being overworked. If not, it can lead it to sluggishly process requests, reject some of them, or even crash.
Let’s delve into some of the ways to optimize your cyber security and monitoring tools using load balancing. You’ll learn how to utilize load balancers for scaling your web service availability, application, scalability, and resilience with additional security.
How Does a Load Balancer Work?
The load balancer employs a predetermined pattern called a load balancing algorithm or approach. This pattern ensures that no server is required to manage more traffic than it can handle.
Various algorithms control the process in different ways. As a result, you have a wide range of alternatives when deciding which kind of load balancer to utilize.
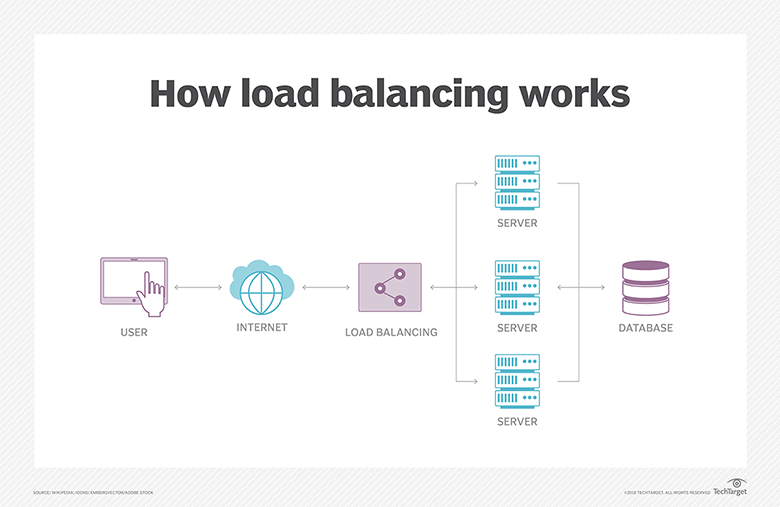
The traditional static approach is the most fundamental form of load balancing. Even with this straightforward solution, you can reduce downtime and performance problems. But to reap the true rewards of load balancing, you need a network packet broker (NPB) that will distribute your packets on an as-needed basis.
An NPB performs a number of calculations for connection and response timing to identify the optimum route for packets. It does this to improve visibility for your out-of-band and in-line security and monitoring tools while minimizing the impact on traffic flow.
How to optimize your cyber security and monitoring tools using load balancing
There are numerous advantages that load balancing provides, especially if your company deals with or manages high-traffic applications, websites, or databases receiving a ton of queries.
Load balancing can optimize:
- Data delivery
- Resource utilization
- Response time
It enables accurate and seamless user requests in high-traffic settings. It saves users from coping with frustrating resources and applications that don't work.
Load balancing is essential for:
- Preventing downtime
- Streamlining security
- Lowering the risk of lost productivity and lost revenue
To avoid server overload, load balancing is by far the best technique for evenly dividing application or website traffic over numerous servers. Let’s explore in detail how load balancing helps optimize your cyber security and monitoring tool.
1. Counter DDoS attacks
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks pose a serious cyber security risk to the contemporary commercial environment. It’s a type of cyber attack where numerous computers bombard a single server with a lot of requests, blocking legitimate requests from other sources.
Any business with a website is susceptible to DDoS attacks since they can affect the functionality of all systems and devices, resulting in up to six-figure losses per hour. A DDoS attack also carries the risk of data loss or theft, malware, and a loss of client confidence in addition to financial loss.
It’s best for any company to include load balancing in a multi-layered protection strategy. This avoids a single point of failure brought on by a DDoS assault, as it provides resilience by rerouting traffic and making the afflicted server inaccessible.
Additionally, load balancing provides an offloading function that directs traffic to public cloud servers, assisting enterprises in reducing the impact of a DDoS attack.
In order to reduce the danger of overload from unexpected traffic, the next-generation load balancers built on software-defined networking (SDN) provide intuitive dashboard features with comprehensive insights for particular applications.
2. Utilize SSL offloading
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a cryptographic system used to secure internet-based communication between clients and servers. However, the encryption and decryption processes require a lot of resources.
SSL offloading involves moving the computational burden of SSL traffic encryption and decryption to dedicated servers with improved application performance.
However, SSL offloading with the assistance of load balancer opens up new possibilities. It’s a crucial defense against hackers as well as man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
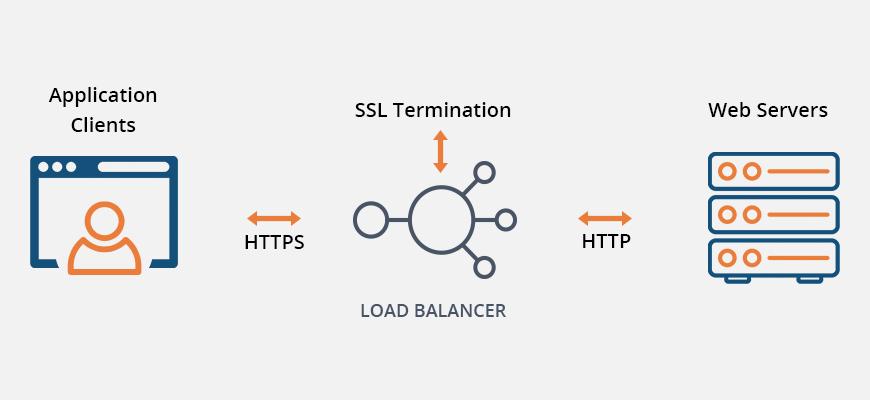
An SSL load balancer is responsible for establishing a secure connection with the clients. It does so by behaving as a mediator on the server side.
Before sending out client queries to the application server, it encrypts the web-server responses and decrypts client requests. Based upon network security between load balancers and servers, the encryption and decryption process varies.
3. Leverage WAF
A web application firewall (WAF) is an essential element of application security against the OWASP Top 10. Proxy-based web application firewalls are a go-to solution through predefined or configurable rules, especially for zero-day vulnerabilities.
There are numerous insertion sites where WAF can be deployed in the data route. Some insertion places are more effective than others, while others are failure points.
Furthermore, WAF requires visibility in order to inspect the entire flow, particularly payloads, because malicious code is inserted within them as opposed to the protocol headers.
Therefore, placing a WAF after a load balancer enables SSL decryption before traffic is forwarded to the WAF. It allows the load balancer to route traffic effectively while keeping some traffic patterns away from APIs and applications.
4. Streamline user authentication
Access based on attributes or identity is a critical component of modern application security. However, the developers keep writing the same authentication code when they move application development to the cloud.
While web developers need social identity providers (IdP) to grant user access, enterprises need on-premise user identity authentication for cloud applications.
By integrating built-in authentication capabilities, application load balancers (ALB) have simplified the user login procedure. Users who access the application are securely authenticated by ALB, saving developers from having to write the code.
5. Prevent performance degradation
Load balancing provides a number of additional approaches to enhance cyber security and monitoring tool performance in addition to automating scaling to improve system performance.
Deploying several small-capacity tools rather than a single expensive tool is an efficient technique to process a lot of data flow using limited-capacity instruments.
The even allocation of traffic between them for load processing is made possible by load balancing. Hence, load balancing assists in performance enhancement and upgrading network security.
6. Implement advanced redundancy schemes
Failure of a network or security monitoring instrument is a typical occurrence. Site outages can happen for a variety of reasons, including operational problems or DDoS attacks. A situation like this necessitates constant degrees of resilience.
One way to enhance cyber security and guarantee device availability is failover. Frequently used in conjunction with load balancing, failover increases fault tolerance and minimizes the harm caused by downtime.
Parallel redundancy or N+1 security monitoring tools disperse the traffic while adhering to the N+1 advanced redundancy method. This distributes the traffic to the remaining N tools when one cannot monitor them.
Maintaining security tools and devices while providing network security monitoring services is also made possible by allocating or redistributing responsibilities for traffic processing among the instruments.
In order to achieve close to zero downtime, you may want to deploy additional load balancers.
7. Facilitate network infrastructure expansion
Load balancing optimizes the easy expansion of network infrastructure. If you want to increase the network infrastructure from 1 to 10 Gb or from 10 Gb to 40 or 100 Gb, load balancers can easily be configured to prevent or stop the upgrading of the network or monitoring tools.
The pace and feed of incoming traffic are impacted by the network infrastructure expansion. In order to maintain flexibility in website security and network administration, load balancing setups are required.
Before selecting a load balancing solution, plan for potential network expansion. A system that manages pool members both centrally and remotely is needed for network infrastructure upgrades, together with a scalable load balancing infrastructure that keeps tools performing as the network expands.
Conclusion
From the user's perspective, load balancing functions as an undetectable mediator between a client and a collection of servers, making sure connection requests are not dropped. Applications, websites, databases, and online services would likely crash without load balancing when demand is too great.
A single busy website might handle hundreds or thousands of user requests concurrently. In order to accurately fill web pages with the desired information, including text, images, video, and audio streaming, many servers are required.
Load balancers should be used as a point of distribution for heavy traffic among numerous servers. It's a smart way to meet compliance requirements and acts as an extra layer of protection while maintaining website scale, performance, and reliability.
The addition and integration of load balancing into other security solutions greatly improves their monitoring capabilities and offers superior overall defense against cyber attacks. Use load balancing to optimize these tools' monitoring performance.
To safeguard your network, use vulnerability monitoring tools as well as attack identification and prevention tools in-house or contract out the work. Protecting your network calls for a system that strictly maintains the high volume of incoming traffic regarding the capabilities of security technologies.













Leave a Reply