The current internet age is witnessing tremendous growth, which can be attributed to the rise in technology and digital advancements. However, this constant growth has a lot of negative repercussions as well.
Cyber attack is one of those repercussions. In fact, we have seen different types of cyber attacks in Cyberspace. Recent cyber attacks in 2018, like Sunburst attack hub and Maze Ransomware, have led to severe consequences.
Before I provide you with a list of different types of cyber-attacks that you should be aware of, let me help you define a cyber attack and how it happens.
What is Cyber Attack?
A cyber attack is an assault launched by criminals that utilize one or more computers to disable computers, steal data, or employ a breached computer as a launch point for other attacks. Cybercriminals utilize different methods to launch a cyber attack, like malware, phishing, ransomware, denial of service, etc.
Several cyber-attacks are opportunistic, where hackers exploit vulnerabilities in a computer system's defenses and start exploiting them. This may include searching for flaws in the code of a website, enabling them to insert their own code, and then bypass security or authentication processes. They can even install ‘malware’ - software specifically designed to damage a system through a vulnerable third-party site.
How Does it Happen?
Cyber attacks typically happen through mundane errors such as a user selecting an easy-to-guess password or not changing the default password on something like a router. Phishing is yet another way to gain access to a system. It involves extracting personal information under false pretenses.
A prime example of that is you may receive a very official-looking email asking you to change your password, which hackers have sent to trick you. Recent cyber attacks like this happened to a top official in a Democratic Party in the run-up to the 2016 US election, resulting in the release of 60,000 private emails.
Another form of networking attack is a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), where vast amounts of traffic are sent to a system to be crashed. A system can handle only a limited number of requests at one time. It’s just like a switchboard receiving too many phone calls, which results in its eventual crash. Once this particular thing occurs, authentic users can no longer access the service.
In simple words, it results in lost revenue for the organization and severe repercussions if the service is essential, for example, the healthcare system.
But there is a significant difference between dangerous cyber attacks and common cyber attacks. Let’s find out the difference in the form of the image given below.

Now that you have understood the meaning of cyber attacks and how it happens, as promised, let’s go to the business end of this write-up to discuss the different types of cyber-attacks, their definitions, practical examples, and the best ways to prevent them.
7 Types of Cyber Attacks You Should Be Aware of
Table of Contents
1. Social Engineering
Definition
Social engineering is a term used for a wide array of ill-intentioned activities that can be accomplished through human interactions. It utilizes psychological ways to manipulate people into making security mistakes or giving away sensitive information.
There are one or more steps needed to make social engineering attacks happen. A perpetrator first scrutinizes the intended victim to accumulate the requisite background information, like the potential points of entry and weak security protocols needed to proceed with the attack. Next, the attacker gains the victim’s trust and provides stimuli for subsequent actions to break security practices like revealing sensitive information or granting access to critical resources.
Social engineering is one of the most exceptionally dangerous types of cyber attacks because it relies on human error instead of vulnerabilities in the software and operating systems. The mistakes made by legitimate users can not be predicted easily, making it harder to determine than a malware-based intrusion.
Examples
Here are some examples of social engineering that emphasize how emotion is utilized to commit malware attacks.
Fear
You get an email that says you’re under scrutiny for tax fraud, and you need to call immediately to prevent arrest and criminal investigation. This type of social engineering attack typically occurs during the tax season when people are already stressed about their taxes. Cybercriminals take advantage of this stress and anxiety and utilize these fear emotions to trick people into complying with their emails.
Greed
Imagine you are given a business proposition of transferring $10 and growing it into $10,000 without any effort from your side. Cybercriminals employ this basic human emotion of trust and greed to persuade victims to get something from literary nothing. A carefully worded baiting email informs victims to provide their bank account details, and the funds will be transferred the same day.
Curiosity
Cybercriminals watch all the global events that capture the attention of the news and then take advantage of human curiosity to trick social engineering victims into acting. For example, the 2nd Boeing Max8 plane crash was a piece of enormous news; cybercriminals took advantage of this attention-grabbing news and sent emails with attachments proclaiming that it included leaked data about the crash. In reality, when the users downloaded the attachment, a version of the HWorm RAT got transmitted to the victim’s computer.
Prevention
Here are some of the tips to prevent social engineering cyber threats from occurring.
- Never open emails and attachments from distrustful sources
- Employ multi-factor authentication
- Always be wary of tempting offers
- Keep your antivirus/antimalware software updated
2. Ransomware
Definition
Ransomware is a malware attack that encrypts a victim's files. The attacker then asks for ransom from the victim to restore access to the data once the payment is received. There are times when the ransom demand comes with a stringent deadline. In case the victim does not pay on time, the data is gone forever.
Ransomware attacks are a part of the list of cyber attacks. Large companies in North America and Europe have fallen victim to it. Cybercriminals will leave no stone unturned while attacking any consumer or business and victims across all industries.
Various government agencies like the FBI advise against paying the ransom as it encourages the attackers to re-do the practice.
Examples
Here are some examples of ransomware that will help organizations gain a solid foundation of most ransomware attacks’ tactics, exploits, and characteristics.
WannaCry
A robust Microsoft exploit was leveraged to create a global ransomware worm that infected more than 250,000 systems before a killswitch was tripped to stop it. Proofpoint was assigned to find the sample employed to search the killswitch and deconstruct the ransomware. To learn more about Proofpoint’s participation in stopping WannaCry, click here.
CryptoLocker
This was the current generation of ransomware wherein the perpetrators demanded cryptocurrency for payment (Bitcoin) and encrypted the user’s the hard drive and attached network drives. CryptoLocker was spread with the help of an email via an attachment that proclaimed to be FedEx and UPS tracking notifications. A decryption tool was utilized for this in 2014. However, reports suggest that more than $27 million was extorted by CryptoLocker.
NotPetya
It’s considered to be one of the most demanding ransomware attacks. NotPetya employed tactics from its namesake Petya, wherein it infected and encrypted the master boot record of a Microsoft Windows-based system. It should be noted that NotPetya employed the same vulnerability as WannaCry to spread swiftly, demanding payment in bitcoin to undo the changes. Some people have even termed it a wiper since NotPetya cannot undo its changes to the master boot record and renders the target system unrecoverable.
Bad Rabbit
You can consider Bad Rabbit to be the long-long cousin of NotPetya as it employs similar code and exploits to spread the ransomware. Bad Rabbit first appeared to target Russia and Ukraine. However, the significant difference with Bad Rabbit is that, unlike NotPetya, it enables decryption if the ransom is paid. The majority of the cases found so far indicate that it was spread through a fake Flash player update that impacts users through drive-by-attack.
Prevention
There are several definitive steps that you can take to prevent ransomware infection. Most of these steps relate to good cybersecurity practices in general, so following them enhances your defenses against all sorts of attacks:
- Ensure that your operating system is patched and up-to-date so that there are fewer vulnerabilities to exploit.
- Never install software or give it administrative privileges until you know what it is and what it does.
- Install antivirus software that assists in detecting malicious programs like ransomware as they come and whistling software, which prevents unauthorized applications from executing in the first place.
- And the most important one is to back up your files regularly and automatically. This won’t stop malware attacks; however, it can make the damage caused by one much less significant.
3. DDOS Attacks
Definition
The DDoS attack, also known as the distributed denial-of-service attack, is a malicious attempt to disrupt the regular traffic of a targeted server, service, or network by overloading the target or its adjoining infrastructure with a flood of internet traffic.
DDoS attacks are one of the lethal types of cyber attacks that achieve effectiveness by employing various compromised computer systems as sources of attack traffic. The exploited machines can include computers and other networked resources like IoT devices.
In simple words, a DDoS attack is similar to an unexpected traffic jam clogging up the highway that prevents regular traffic from arriving at its destination.
Examples
Here are some of the live DDoS attacks to date.
The Google Attack, 2000
On October 16, 2020, when Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) posted a blog discussing how the threats and threat actors are changing their tactics due to the 2020 U.S. election. It was launched from three Chinese ISPs; the attack on thousands of Google’s IP addresses lasted for six months and peaked at a breath-taking 2.5 Tbps.
The AWS DDoS Attack in 2020
A massive DDoS attack hit Amazon Web Services in February 2020. This was the most lethal DDoS attack ever, and it targeted an unidentified AWS customer employing a technique known as Connectionless Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (CLDAP) Reflection.
This technique relies heavily on unguarded third-party CLDAP servers and increases the amount of data sent to the victim’s IP address by 56 to 70 times. Such was the propensity of these network attacks that it lasted for nearly three days and peaked at a remarkable 2.3 terabytes per sound. This was one of AWS's most lethal cyber security threats to date.
Prevention
- Take swift action.
- Employ anti-DDoS services that aid you in recognizing legitimate spikes in network traffic and a DDoS attack.
- If you find your company is under attack, notify your ISP provider at the earliest to determine if your traffic can be re-routed.
- Having a backup ISP is also a fantastic option.
- Configure firewalls and routers to reject bogus traffic and keep your firewalls and routers updated with the latest security patches.
- Employ AI to develop new systems that can quickly route internet traffic to the cloud, where it’s scrutinized, and the malicious web traffic can be blocked before it reaches the computers of the company.
- AI programs can ascertain and defend against known DDoS indicative patterns. In addition to this, AI can aid in predicting and ascertaining future DDoS patterns.
- Secure your IoT devices by keeping secured passwords and a strong firewall.
4. Malware
Definition
Malware Software, or just Malware, is a blanket term used to describe viruses, worms, trojans, and other harmful computer programs hackers use to create havoc and destruction by gaining access to sensitive data. It’s one of those types of cyber attacks seen more frequently in the practical world nowadays.
Examples
Here are some real-life cases of malware attacks.
CovidLock, ransomware, 2020
Cybercriminals have widely exploited the fear of Coronavirus. CovidLock ransomware is one of the prime examples of it. This type of ransomware infects victims' systems through malicious files, promising more information about the disease. Once installed, CovidLock encrypts data from Android devices and denies data access to victims. To get access, victims have to pay a ransom of $100 per device.
Zeus, trojan, 2007
Zeus is a Trojan distributed via malicious files hidden in emails and fake websites in cases involving phishing. It’s widely known to copy keystrokes leading to credential and password thefts for bank accounts and email accounts. Zeus has already hit reputed companies like Amazon, Bank of America, and Cisco. The damage caused by Zeus is reported to be more than $100 million since its emergence in 2007.
MyDoom, worm, 2004
In 2004, MyDoom worm became widely recognized for hitting major technology companies like Microsoft and Google. An email was used to target it by employing attention-grabbing subjects like “Error,” “Mail Delivery System,” and “Test.” MyDoom was employed for DDoS attacks as a backdoor to enable remote control. The losses incurred as a result of this worm are estimated to be in millions of dollars.
Prevention
- Train users on best practices to avoid malware
- Use reputable A/V software
- Ensure that your network is secure
- Perform regular website security checks
- Create verified, regular backups
5. MITM Attack
Definition
MitM attacks, also known as Man-in-the-middle attacks, are common cyber security threats that enable attackers to eavesdrop on the conversation between two targets. The attack takes place between two legitimately communicating hosts, allowing the attacker to “listen” to a conversation they should typically not be able to listen to; hence, the name of this threat is “man-in-the-middle.” It is one of those types of cyber attacks that can dupe a person quickly.
For example, Victor and Charles are having a conversation. Andrew wants to eavesdrop on the conversation but also remain transparent. Now, Andrew could tell Victor that she is Charles and tell Charles she is Victor. This would lead Victor to believe he’s speaking to Charles, revealing his part of the conversation to Andrew. Andrew would then gather information from this, alter the response, and pass the message to Charles (who thinks he’s talking to Victor). As a result, Andrew can transparently hijack their conversation.
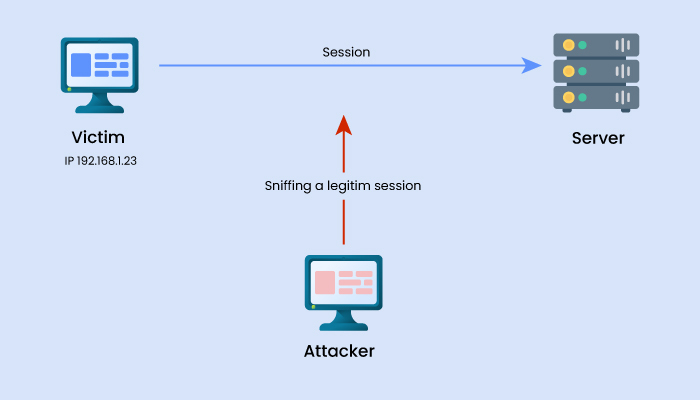
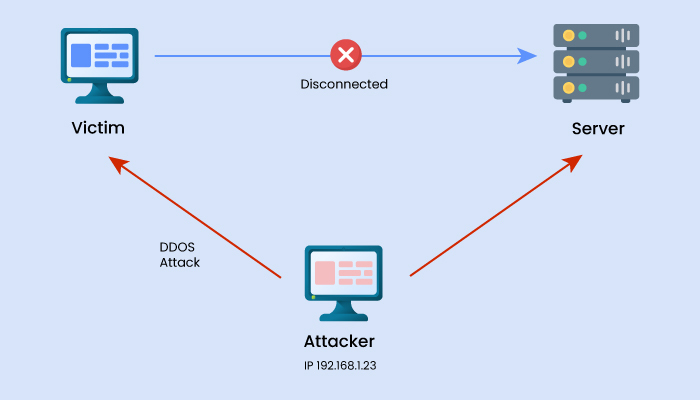
Examples
Here’s a real-life MitM attack that took place in 2011.
A Dutch registrar site DigiNotar was breached, allowing a threat actor to access 500 certificates for reputed sites like Google, Skype, etc. Through access to these certificates, the attacker posed as a legitimate website causing a MitM attack and stealing the data of users after tricking them into entering passwords on malicious mirror sites. Due to this breach, DigiNotar ultimately filed for bankruptcy.
In 2017, credit company Equifax removed its app from Google and Apple after a breach resulted in personal information leaks. A researcher learned that the apps did not employ HTTPS, enabling attackers to intercept data as users accessed their accounts.
Prevention
- Have a robust encryption mechanism on wireless access points to prevent unwanted users from joining your network simply by being nearby.
- Have strong router login credentials.
- Use VPNs to create a secure environment for sensitive data within a local area network.
- Use HTTPS and do not provide HTTP alternatives for websites and applications. To enable HTTPS on the website, you need to purchase it first. Select the website type and number of domains and buy SSL certificate according to it. Different SSL providers are there who can give you a handsome discount on the purchase of your SSL certificate.
- Have public key pair-based authentication like RSA to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
6. Password Attack
Definition
Password is the most widely used mechanism to authenticate a user to a system. Consequently, the act of obtaining someone else’s password is a common and effective form of attack. This is known as a password attack. It’s one of the most common cyber attacks in this digital era.
Example
You can gain a person’s password by looking around a person’s desk. More often than not, they leave their passwords in plain sight or on their desk.
Perpetuators even sniff the connection between a user’s computer by employing a network. They can then take advantage of this and track an individual's password. This method requires the network connection to be unprotected. An unprotected network connection can easily be hacked. Hence, never visit a site with HTTPS that needs a password. You can also get the password by gaining access to the password database.
Hackers even utilize brute- force by randomly guessing passwords. This can be done by using the person’s name, job title, hobbies, etc.
The last attack is a dictionary attack. A dictionary of common passwords can be used to gain access. In case the hacker has a copy of the encrypted password file from a system, they could use the same encryption to a dictionary of commonly used passwords to compare the results.
Prevention
- The best way to prevent password attacks is by adopting the best password hygiene and management practices.
- Ensure that your password is long and complex for every website or account.
- Execute multi-factor authentication whenever possible
- Adopt a password manager to simplify password management and ensure secure storage
7. SQL Injection Attack
Definition
With the help of a successful SQL injection attack, perpetrators can get unauthorized access to sensitive data like passwords, credit card information, or personal user information. SQL injection attack results in reputational damage and regulatory fines. Sometimes, an attacker can get a persistent backdoor into an organization’s systems, resulting in a long-term compromise that can go undetected for a long time. It’s one of the most lethal types of cyber attacks that can wreck an organization without even letting them know what hit them.
Example
Here are a few real-life SQL injection attacks targeted at large websites, businesses, and social media platforms:
GhostShell attack
Hackers from the APT group team GhostShell targeted 53 universities employing SQL injection and stole and published 36,000 personal records which belonged to students, faculty, and staff.
Turkish government
Another APT group, RedHack collective, employed SQL injection to breach the Turkish government website and erase debt to government agencies.
7-Eleven breach
A team of attackers employed SQL injection to get into corporate systems at several companies, primarily the 7-Eleven retail chain, stealing 130 million credit card numbers.
Prevention
- Use parameterized queries (also known as prepared statements) instead of string concatenation within the query.
- Ensure that the string used in the query is always a hard-coded constant.
- It must never contain any variable data from any origin.
The Future of Cybersecurity in 2021 and Beyond
Cyber threats have grown in prominence in recent years. And with that, the complexity of their attack has also become exponentially larger with the advent of the internet and now with the emergence of the Internet of Things (IoT).
Here’s what the future holds for cyber security as we head to 2021 and beyond.
- The trend of more ransomware threats will continue.
- USB devices can prove to be a more potent threat to PCs in the digital era than ever before.
- With remote working becoming more of a norm, we will see a uni-purpose laptop for critical remote workers capable of performing only a single task and won’t have access to emails, social media, or any public network connections.
The list of cyber attacks that you will see in 2021 and beyond will not be less. Still, with the help of the ideas I mentioned above, you can always minimize networking attacks and cyber threats by becoming more vigilant and prepared for the future. I hope you have as much fun reading the types of cyber attacks as I had while preparing them for you.
For more information on the latest technologies, keep reading this section!













Leave a Reply